>> f = sym('x')f =x>> whosName Size Bytes Class Attributesf 1x1 112 sym >>
符号表达式的加、减、乘、除、幂运算与一般的数值运算一样,分别用“+”、“-”、“*”、“/“、”^“来进行运算。
>> f = sym('x')f =x>> g = sym('x^2')g =x^2>> f+gans =x+x^2>> f*gans =x^3>> f^gans =x^(x^2)>> 2.符号表达式的提取分子和分母运算
如果符号表达式是一个有理分式或可以展开为有理分式,可利用numden函数来提取符号表达式中的分子或分母。其一般调用格式为:
[n,d]=numden(s)
该函数提取符号表达式s的分子和分母,分别将它们存放在n与d中。
>> f = sym('a*x^2+b*x/(a-x)');
>> [n,d]=numden(f)n =x*(-a^2*x+a*x^2-b)d =-a+x>> 3.符号表达式中变量的确定
MATLAB中的符号可以表示符号变量和符号常数。findsym可以帮助用户查找一个符号表达式中的符号变量。该函数的调用格式为:
findsym(S,n)
函数返回符号表达式S中的第n个符号变量,若没有指定n,则返回S中的全部符号变量。
在求函数的极限、导数和积分时,如果用户没有明确指定自变量,MATLAB将按缺省原则确定主变量并对其进行相应微积分运算。可用findsym(S,1)查找系统的缺省变量,事实上,MATLAB按离字符'x'最近原则确定缺省变量。
>> f = sym('x^2+y+z')f =x^2+y+z>> findsym(f)ans =x, y, z>> 3.复合函数计算
在MATLAB中符号表达式的复合函数运算主要是通过函数compose来实现的。compose函数的调用格式如下:
调用格式 说明
compose(f,g) 返回复合函数f(g(y))。在这里f=f(x),g=g(y)。其中x是findsym定义的f函数的符号变量,y是findsym定义的g函数的符号变量
compose(f,g,z) 返回自变量为z的复合函数f(g(z))。在这里f=f(x),g=g(y)。其中x、y分别是findsym定义的f函数和g函数的符号变量
compose(f,g,x,z) 返回复合函数f(g(z)),并使x成为f函数的独立变量(意思是如果f有多个变量指定x为其变量)。即,如果f=cos(x/t),则compose(f,g,x,z)返回cos(g(z)/t)
compose(f,g,x,y,z) 返回复合函数f(g(z)),并使x与y分别成为f与g函数的独立变量。即如果f=cos(x/t),g=sin(y/u),则compose(f,g,x,y,z)返回cos(sin(z/u)/t),而 compose(f,g,x,u,z)返回cos(sin(y/z)/t)
>> syms x y z t u;
>> f = 1 + x^2;
>> g = sin(y);
>> h = x^t;
>> p = exp(-y/u);
>> compose(f,g)ans =1+sin(y)^2>> compose(f,g,t)ans =1+sin(t)^2>> compose(h,g,x,z)ans =sin(z)^t>> compose(h,g,t,z)ans =x^sin(z)>> compose(h,p,x,y,z)ans =exp(-z/u)^t>> compose(h,p,t,u,z)ans =x^exp(-y/z)>> 4.反函数计算
在MATLAB中符号表达式的反函数运算中主要是通过函数findverse来实现的。findverse函数的调用格式
调用格式 说明
g=findverse(f) 返回符号函数f的反函数,其中f是一个符号函数表达式,其变量为x。所求的反函数是一个满足g(f(x))=x的符号函数
g=findverse(f,v) 返回自变量为v的符号函数f的反函数,所求的反函数g是一个满足g(f(v))=v的符号函数。当f包含不止一个变量时,往往用这种反函数调用格式
>> syms x y;
>> f = x^2 + y;
>> finverse(f,y) %regard y as variable,x as constantans =-x^2+y>> finverse(f)
Warning: finverse(x^2+y) is not unique.
> In sym.finverse at 43ans =(-y+x)^(1/2)>> 5.求表达式的和
在MATLAB中,求表达式的符号和主要是通过函数symsum来实现的。symsum函数的调用格式如下:
调用格式 说明
symsum(S) 返回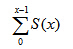
symsum(S,v) 返回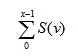
symsum(S,a,b) 返回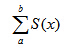
symsum(S,v,a,b) 返回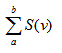
>> x = sym('x');
>> symsum(x)ans =1/2*x^2-1/2*x>> 6.符号表达式、字符串、数值之间的转换
(1)将符号表达式转换成数值表达式可以通过函数eval来实现,其中eval函数也可以将字符串转换成数值表达式
>> n = 4;
>> syms i j
>> t = 1/(i+j-1)t =1/(i+j-1)>> a = zeros(n);
>> for i = 1:n
for j = 1:n
a(i,j) = eval(t);
end
end
>> aa =1.0000 0.5000 0.3333 0.25000.5000 0.3333 0.2500 0.20000.3333 0.2500 0.2000 0.16670.2500 0.2000 0.1667 0.1429
或者将t写成字符串的形式
>> n = 4;
>> t = '1/(i+j-1)';
>> a = zeros(n);
>> for i = 1:n
for j = 1:n
a(i,j) = eval(t);
end
end
>> aa =1.0000 0.5000 0.3333 0.25000.5000 0.3333 0.2500 0.20000.3333 0.2500 0.2000 0.16670.2500 0.2000 0.1667 0.1429>>
(2)将数值表达式转换成符号表达式主要是通过函数sym来实现的。
>> p = 1.74p =1.7400>> q = sym(p)q =87/50>> 另外,函数poly2sym可以实现将MATLAB等价系数向量转换成它的符号表达式。
>> a = [1 3 4 5]a =1 3 4 5>> p = poly2sym(a)p =x^3+3*x^2+4*x+5>>
(3)符号表达式与字符串的相互转换
符号表达式转字符串可以通过char函数,字符串转符号表达式可以通过sym函数
>> f = 'x+y'%此时f为字符串f =x+y>> f = sym(f)%此时f为符号表达式f =x+y>> f = char(f)%此时f为字符串f =x+y>>
7.符号表达式(符号矩阵)的因式分解
符号表达式因式分解通过函数factor来实现,其调用格式如下:
factor(s)
如果输入变量s为一符号矩阵,则此函数将因式分解此矩阵的各个元素。
>> syms x
>> factor(x^9 - 1)ans =(x-1)*(x^2+x+1)*(x^6+x^3+1)>> factor(sym('12345678901234567890'))ans =(2)*(3)^2*(5)*(101)*(3803)*(3607)*(27961)*(3541)>> 8.符号表达式(符号矩阵)的展开
符号表达式的展开可以通过函数expand来实现,其调用格式如下
expand(s)
此函数经常用在多项式的表达式中,也常用于三角函数、指数函数、对数函数的展开中。
>> syms x y
>> expand((x+3)^4)ans =x^4+12*x^3+54*x^2+108*x+81>> expand(cos(x+y))ans =cos(x)*cos(y)-sin(x)*sin(y)>> 9.符号表达式(矩阵)的合并运算
collect(s) 对s合并同类项,s是符号表达式或符号矩阵。即将符号表达式s写成关于默认变量的幂形式,默认变量由findsym来确定。
collect(s,v) 对s按变量v合并同类项,s是符号表达式或符号矩阵。即将符号表达式s写成关于v的幂形式。
>> syms x y
>> collect(x^2*y + y*x - x^2 - 2*x)ans =(y-1)*x^2+(y-2)*x>> f = -1/4*x*exp(-2*x)+3/16*exp(-2*x);>> collect(f,exp(-2*x))ans =(-1/4*x+3/16)*exp(-2*x)10.符号表达式(矩阵)的简化
符号简化可以通过函数simple和simplify来实现。这两个函数的调用格式。
调用格式 说明
simple(s) 对表达式s尝试多种不同算法简化,以显示s表达式的长度最短的简化形式;若s为一矩阵,则结果是全矩阵的最短形行,而非每个元素的最短形
[R HOW]=simple(s) 返回的R为简化型,HOW为简化过程中使用的方法
simplify(s) 简化符号表达式
>> help simple--- help for sym/simple.m ---SIMPLE Search for simplest form of a symbolic expression or matrix.SIMPLE(S) tries several different algebraic simplifications ofS, displays any which shorten the length of S's representation,and returns the shortest. S is a SYM. If S is a matrix, the resultrepresents the shortest representation of the entire matrix, which is not necessarily the shortest representation of each individual element.[R,HOW] = SIMPLE(S) does not display intermediate simplifications,but returns the shortest found, as well as a string describingthe particular simplification. R is a SYM. HOW is a string.Examples:S R Howcos(x)^2+sin(x)^2 1 simplify2*cos(x)^2-sin(x)^2 3*cos(x)^2-1 simplifycos(x)^2-sin(x)^2 cos(2*x) combine(trig)cos(x)+(-sin(x)^2)^(1/2) cos(x)+i*sin(x) radsimpcos(x)+i*sin(x) exp(i*x) convert(exp)(x+1)*x*(x-1) x^3-x combine(trig)x^3+3*x^2+3*x+1 (x+1)^3 factorcos(3*acos(x)) 4*x^3-3*x expandsyms x y positivelog(x) + log(y) log(x*y) combineSee also simplify, factor, expand, collect.Reference page in Help browserdoc simple>> help simplify--- help for sym/simplify.m ---SIMPLIFY Symbolic simplification.SIMPLIFY(S) simplifies each element of the symbolic matrix S.Examples: simplify(sin(x)^2 + cos(x)^2) is 1 .simplify(exp(c*log(sqrt(alpha+beta))))See also simple, factor, expand, collect.Reference page in Help browserdoc simplify
11.符号表达式的分式通分
求解符号表达式的分子和分母可以通过函数numden来实现,其调用格式如下:
[n,d]=numden(A)
可以把A的各元素转换为分子和分母都是整系数的最佳多项式型。
>> syms x y
>> [n,d] = numden(x/y - y/x)n =x^2-y^2d =y*x>> 12.符号表达式的“秦九昭型“重写
符号表达式的”秦九昭型“重写可以通过函数horner(P)来实现,其调用格式如下:
horner(P)
可以将符号多项式转换成嵌入套形式表达式。
>> horner(x^4-3*x^2+1)ans =1+(-3+x^2)*x^2>>

 支付宝扫一扫
支付宝扫一扫 微信扫一扫
微信扫一扫











.png)


